Generative AI in Business Intelligence: How It Works, Use Cases, and Real Impact
Generative AI in business intelligence explained in simple terms. How it works, how it differs from traditional AI, real BI use cases, benefits, and risks.

How modern generative AI works and why it matters for business intelligence
Generative AI feels like it appeared overnight. One day it was research papers and demos, and the next day it was writing emails, explaining dashboards, designing images, and answering customer questions.
Tools like ChatGPT made this shift visible to everyone, but generative AI itself is neither magic nor brand new. It is the result of decades of research, combined with massive data, powerful computing, and interfaces that finally feel natural to use.
This updated guide explains generative AI in clear terms: what it is, how it works, how it differs from traditional AI, and why generative AI in business intelligence is reshaping how organizations understand data without replacing human judgment.
What Is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence designed to create new content based on patterns learned from data.
Unlike traditional AI systems that focus on classification or prediction, generative AI produces original outputs that resemble its training data. These outputs can include:
Text such as summaries, reports, explanations, or answers
Images and visual designs
Audio, music, or speech
Code and technical documentation
Written insights generated from data
A simple way to understand the difference:
Traditional AI answers questions like:
Is this transaction fraudulent?
Generative AI answers questions like:
Explain why this trend happened and what might happen next.
Traditional AI behaves like a calculator.
Generative AI behaves like an assistant that explains results in human language.
Why Generative AI Feels So Different
Before generative AI became popular, most people interacted with AI indirectly. Models worked in the background, scoring risks, ranking results, or powering dashboards.
Generative AI changed the interface.
Instead of clicking through menus, users can ask questions. Instead of reading charts, they can receive written explanations. This shift makes advanced systems accessible to people without technical backgrounds.
The core technology is still machine learning, but the experience feels more human.
A Brief History of Generative AI
Generative AI may feel new, but its foundations stretch back decades.
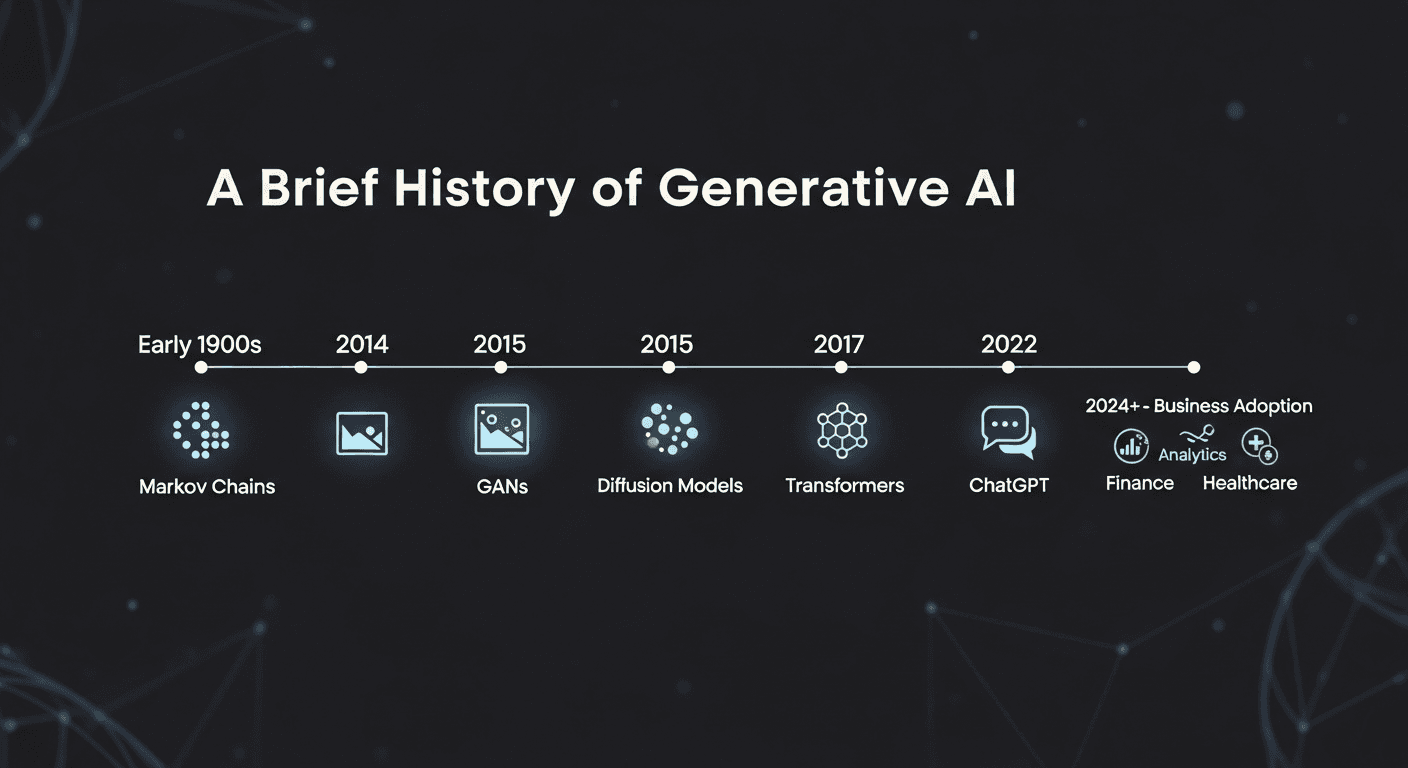
Early probability based models such as Markov chains were used for basic text prediction in the early 20th century
In 2014, Generative Adversarial Networks enabled realistic image generation
In 2015, diffusion models introduced a new way to generate high quality images by iterative refinement
In 2017, transformer architectures transformed how machines understand language and context
In 2022, ChatGPT brought large language models into everyday use
From 2024 onward, businesses began embedding generative AI into analytics, finance, healthcare, and operations
The breakthrough was not a single invention. It was the combination of scale, data availability, and usable products.
How Generative AI Works
At a high level, most generative AI systems follow three steps.
1. Training on Large Datasets
Models are trained on massive collections of text, images, or other data. They do not memorize information like a database. Instead, they learn statistical relationships.
This training teaches the model what patterns commonly appear together.
2. Learning Probabilities and Structure
The model learns things such as:
Which words tend to follow other words
How visual elements form recognizable objects
Which data patterns often co occur
Because the system predicts what is likely, not what is true, it can sometimes sound confident while being incorrect.
3. Generating Outputs Step by Step
When you enter a prompt, the model predicts the most likely next token. It repeats this process many times until a complete response is formed.
This explains both the power and the limitations of generative AI.
Generative AI vs Traditional AI
Aspect | Traditional AI | Generative AI |
Core purpose | Analyze and predict | Create new content |
Typical outputs | Scores, labels, forecasts | Text, images, explanations |
Interaction style | Dashboards and rules | Conversational interfaces |
BI usage | Metrics and alerts |
Generative AI does not replace traditional AI. It extends it by adding a human friendly layer.
Why Generative AI Matters
The importance of generative AI is not just speed or automation.
It changes how work feels.
Used responsibly, generative AI:
Reduces repetitive cognitive effort
Makes complex systems easier to use
Helps people focus on decisions instead of mechanics
Not everything slow should be automated. Thinking, writing, and analysis often take time for a reason.
The real value of generative AI appears when it improves clarity and understanding, not when it removes human involvement.
How Generative AI Is Changing Business Intelligence
Traditional business intelligence tools rely on dashboards, filters, and charts. These tools are powerful, but they often require technical skills.
Generative AI in business intelligence shifts analytics from static dashboards to interactive systems that explain data in plain language and adapt to how people ask questions.
Generative AI is reshaping BI in three important ways.
From Clicks to Conversations
Users can ask questions such as:
Why did revenue drop last quarter?
Which region is underperforming and why?
What changed compared to last year?
The system translates these questions into analytical logic and returns explanations.
Automated Insight Explanation
Generative AI can summarize trends, explain anomalies, and suggest follow up questions. This reduces dependency on SQL or complex reporting workflows.
An Assistant, Not a Replacement
Generative AI works best as a layer on top of dashboards. It helps people understand data faster without replacing core analytics tools.
This supports analysts rather than eliminating them.
Real World Uses of Generative AI
Many people already use generative AI without labeling it as such.
Common examples include:
Chatbots that explain information or answer questions
Writing assistants for emails and reports
Analytics tools that describe trends in plain language
Design tools that generate images or layouts
The value comes from reduced friction, not full automation.
Industry Use Cases
Finance: Fraud Detection
Fraud detection is one of the most practical and high impact applications of generative AI in finance.
Traditional fraud systems rely on historical rules and labeled examples. The problem is that fraud constantly changes. New patterns appear faster than real world data can be labeled.
Generative AI helps close this gap by creating realistic synthetic examples of fraudulent transactions. These synthetic samples are used to train and strengthen machine learning models, improving their ability to distinguish between legitimate and suspicious behavior.
By learning a broader range of fraud patterns, these systems can:
Detect suspicious activity earlier
Reduce false positives that block legitimate customers
Adapt faster to new fraud techniques
This leads to stronger security, lower financial losses, and higher customer trust.
Real world example
Mastercard faced growing fraud risks as criminals increasingly exploited stolen payment card data. To respond faster, Mastercard applied generative AI across transaction data from millions of merchants.
The system learned complex transaction patterns and helped predict which cards were likely compromised, allowing banks to block them before large scale damage occurred.
Results achieved:
Detection of compromised cards doubled
False positives were reduced by up to 200 percent
Merchant fraud detection speed increased by nearly 300 percent
This example shows how generative AI does not replace existing fraud systems, but amplifies them by improving learning, speed, and accuracy. "Source"
The Role of the Generative AI Data Professional
A generative AI focused data professional blends technical skills with judgment.
Important capabilities include:
Understanding machine learning fundamentals
Crafting and evaluating prompts
Interpreting outputs critically
Recognizing bias and ethical risks
AI will not replace people. People who know how to work with AI responsibly will replace those who do not.
Benefits of Generative AI
When applied thoughtfully, generative AI can:
Speed up access to insights
Improve accessibility for non technical users
Enhance creativity and exploration
Reduce repetitive work
The benefits depend entirely on how the technology is used.
Limitations and Risks
Generative AI has real weaknesses that must be understood.
Hallucinations and incorrect outputs
Bias inherited from training data
Over reliance that weakens critical thinking
Security and misinformation risks
Copyright and ownership concerns
These risks make human review essential.
Hype vs Reality
Generative AI is powerful, but automation is not always progress.
Efficiency does not automatically equal quality. Some tasks are valuable precisely because they require time and thought.
Using generative AI well means setting boundaries, not removing responsibility.
How Generative AI Fits Into the Bigger AI Picture
Artificial Intelligence is the broad field
Machine Learning refers to systems that learn from data
Generative AI is a subset focused on creating new outputs
Generative AI is a layer on top of existing systems, not a replacement for them.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is generative AI in business intelligence?
Generative AI in BI creates human-readable insights from complex data, explaining trends, anomalies, and patterns, making analytics accessible to non-technical users while supporting faster, informed decision-making.
2. How does generative AI work in BI?
It trains on large datasets, learns patterns, and generates outputs like reports or explanations in natural language, translating complex analytics into understandable insights for decision-makers.
3. Can generative AI replace data analysts?
No. It enhances analysts’ work by automating repetitive tasks and summarizing insights, but human judgment, domain knowledge, and critical thinking remain crucial for accurate decisions.
4. What industries benefit most from generative AI in BI?
Finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing gain value through fraud detection, predictive maintenance, personalized customer insights, and operational efficiency improvements powered by AI-driven explanations and guidance.
5. Is generative AI safe for sensitive data?
Yes, when combined with proper access controls, anonymization, validation, and human oversight. Responsible usage ensures security, compliance, and ethical handling of business-critical information.
6. How is generative AI different from traditional AI?
Traditional AI predicts or classifies data, whereas generative AI produces explanations, summaries, or new content, enabling interactive and human-friendly BI insights beyond static dashboards.
7. How can beginners start using generative AI in BI?
Start with AI-powered dashboards or analytics assistants, experiment with natural language queries, learn prompt design, and review outputs critically to build practical generative AI skills.
Conclusion
Generative AI is one of the most influential technologies of this era.
Used with intention, it improves clarity, reduces friction, and supports better decisions. Used blindly, it risks dependency and poor judgment.
Generative AI in business intelligence is one of the most influential shifts in how organizations analyze data and make decisions in this era.
The future does not belong to AI alone. It belongs to people who know how to use AI responsibly, thoughtfully, and with purpose.