What Is Data Modeling? Types,Tools, Best Practices, and Real-World Examples
Learn what data modeling is, its types, benefits, tools, and real-world examples. A beginner-friendly, SEO-optimized guide to building scalable data models.

Introduction
When I first came across data modeling, I admit, I thought it sounded a bit too technical, just another step in the world of databases. But the more I worked with it, the more I realized it’s like the backbone of any well-organized data system. A good data model makes information easy to access and understand. A messy model can turn a strong database into a problem.
Whether you’re creating a new database or trying to make sense of an existing one, understanding data modeling is what helps your data actually work for you.
In this post, I’ll walk you through key techniques, best practices, and real-world examples to help you build data models that make your work and your data much easier.
What is Data Modeling?
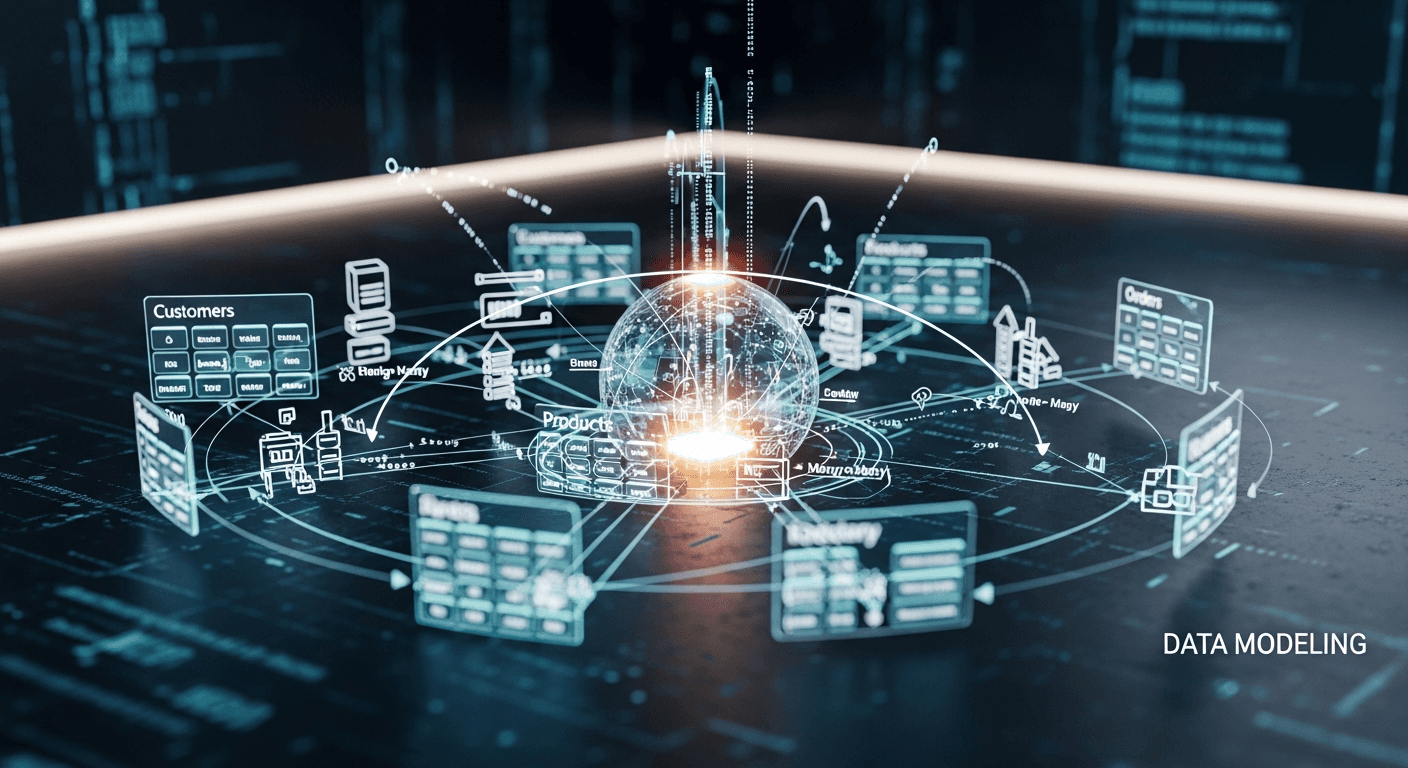
A data model is like a blueprint for a database, it shows how all the information is organized and how different pieces of data are connected. Data modeling helps at every stage of building a database, from planning to implementation.
In simple terms, data modeling is the process of understanding what data a business or application needs, and then organizing it in a clear, visual way so it can be easily used. The resulting data model acts as a guide, showing how different types of information relate to each other.
Example:
Imagine you run an online store. You have three main types of data: customers, orders, and products. A data model helps you see how these pieces are connected:
Each customer can place many orders.
Each order can include many products.
Each product can appear in multiple orders.
This visual map (the data model) makes it easy to understand how all your information fits together. It ensures nothing gets lost or mixed up and helps your database work efficiently, making it easier to track sales, manage inventory, and serve your customers better.
Why Is Data Modeling Important?
Data modeling plays a critical role in both operational and analytical systems:
Reduces data redundancy and inconsistencies
Improves database and query performance
Enables accurate reporting and analytics
Makes systems easier to maintain and scale
Aligns technical teams with business goals
Without proper data modeling, organizations often face slow dashboards, broken reports, and unreliable insights.
Types of Data Models
1. Conceptual Data Models
Conceptual data models give a high-level view of the data without going into technical details. They focus on what data is needed and how different entities relate to each other from a business perspective.
Used in early planning stages
Defines main entities (like customers or orders)
Captures business rules and domain concepts
2. Logical Data Models
Logical data models add more detail while still staying independent of any specific database.
Shows detailed relationships between entities
Defines attributes (fields) for each entity
Uses standard modeling rules and notation
Helps translate business requirements into a structured format
3. Physical Data Models
Physical data models represent how data is actually stored in a database.
Database-specific implementation
Includes tables, columns, keys, and indexes
Focuses on performance, storage, and optimization
Used by developers and database administrators
Examples of Popular Data Modeling Tools
Different tools support different stages of data modeling, from early design to analytics and reporting. Here are some commonly used tools and where they fit best:
ERwin: A widely used enterprise-grade data modeling tool for designing and managing logical and physical database schemas, especially in large organizations with complex data environments.
Lucidchart / Draw.io: Easy-to-use visual diagramming tools ideal for creating conceptual data models and ER diagrams, often used during early planning and stakeholder discussions.
dbt (data build tool): A modern analytics engineering tool used for data transformation and analytics modeling, helping teams define business logic directly within the data warehouse.
Power BI / Looker, Supaboard: Business intelligence platforms that support analytical data models for reporting, dashboards, and metrics, primarily focused on consumption rather than database design.
Common Data Modeling Approaches
Hierarchical Data Models
Hierarchical data models organize data in a tree-like structure, where each record has a single parent and can have multiple child records. This model works well for one-to-many relationships, such as organizational structures or file systems.
Relational Data Models
Relational data models store data in tables made up of rows and columns. These tables are connected using keys and are commonly accessed using SQL. This is the most widely used model in modern databases because it is flexible, reliable, and easy to maintain.
Entity-Relationship (ER) Models
ER models use visual diagrams to show entities and the relationships between them. They make it easier to understand how data is connected and are often used during the planning and design stages of database development.
Object-Oriented Data Models
Object-oriented data models organize data using classes and objects, similar to how data is handled in object-oriented programming. They are useful for managing complex data structures and relationships.
Dimensional Data Models
Dimensional data models are designed for analytics and reporting. They use star and snowflake schemas to organize data in a way that makes querying faster and easier, especially in data warehouses and BI tools.
Benefits of Data Modeling
Get everyone on the same page
Data modeling creates a shared understanding of data across technical and non-technical teams, enabling better collaboration, clearer discussions, and solutions that truly align with real business needs.
Improve data quality
By defining clear rules and relationships, data modeling reduces duplication, errors, and missing information, ensuring reliable data that supports accurate reporting and confident, data-driven decisions.
Improve database performance
A well-structured data model improves database efficiency, simplifies maintenance, and makes it easier to identify bottlenecks and optimization opportunities as data volumes and usage grow.
Prepare your business for what’s next
A strong data model provides flexibility for future changes, making upgrades, scaling, and new technology adoption smoother, faster, and more cost-effective with minimal disruption.
Data Modeling Tools and Technologies
Popular Commercial and Open-Source Solutions
Data modeling tools help businesses design, visualize, and manage database structures efficiently. Commercial tools are commonly used in enterprise environments, while open-source tools are ideal for beginners and cost-effective projects.
Key Features to Consider When Selecting Tools
When choosing a data modeling tool, consider ease of use, visual modeling support, database compatibility, collaboration features, version control, and integration with BI and analytics platforms.
Common Questions and Use Cases
How Can AI Help Generate Logical Data Model Diagrams?
AI-powered data modeling tools can automatically analyze datasets and business requirements to generate logical data model diagrams. They help identify entities, attributes, and relationships faster, reducing manual effort and design errors.
Is Data Modeling in Excel and Power BI the Same Thing?
No. Excel and Power BI data modeling is mainly used for reporting and analysis, while database data modeling focuses on designing structured schemas. Power BI supports basic relationships but cannot replace full logical or physical modeling.
What Is a Data Model in DBMS?
In a DBMS (Database Management System), a data model defines how data is structured, stored, and connected. It includes tables, relationships, keys, and constraints that ensure data accuracy and consistency.
Real-World Applications of Data Modeling
Data modeling is widely used in e-commerce, healthcare, finance, SaaS, and analytics to organize data, improve reporting performance, enable BI dashboards, and support scalable database design.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is data modeling?
Data modeling is the process of organizing and structuring data visually, showing relationships between entities, to improve database efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making.
2. How can I use AI to generate logical data model diagrams?
AI tools can analyze datasets and business requirements to automatically create logical diagrams, identifying entities, attributes, and relationships, reducing manual effort and design errors.
3. What are the main types of data models?
The main types are conceptual (high-level view), logical (detailed relationships and attributes), and physical (database-specific implementation with tables, keys, and indexes).
4. Why is data modeling important for businesses?
It improves data quality, reduces redundancy, ensures accurate reporting, enhances performance, aligns teams with business goals, and supports scalable, efficient database design for future growth.
Conclusion
Data modeling is the foundation of reliable data systems. By following best practices and adapting to future trends, organizations can build data models that support performance, analytics, and long-term business growth.