SQL vs NoSQL Databases: How to Choose the Right Database for Your Business in 2025 and Beyond
In 2025, businesses face an unprecedented data explosion. From AI-driven analytics to real-time user experiences, the database you select underpins every business decision. Choosing the wrong one can create performance bottlenecks, spiraling costs, and compliance issues. Choosing wisely ensures scalability, innovation, and competitive advantage. The key question is SQL or NoSQL.

Understanding SQL and NoSQL Databases
SQL Databases
SQL databases, such as PostgreSQL, MySQL, and Oracle, store data in structured tables with predefined schemas. They follow ACID compliance (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability), making them ideal for transactional workloads.
NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, and Neo4j, are schema-flexible. They store data as documents, key-value pairs, graphs, or wide columns. NoSQL databases are designed for scale and speed, making them perfect for unstructured or rapidly changing data.
Hybrid or Multi-Model Databases
Databases like CockroachDB and Azure Cosmos DB combine relational structure with distributed cloud-scale performance. They allow businesses to handle both transactional and analytical workloads effectively.
Takeaway
Choose SQL for structured, transaction-heavy applications and NoSQL for fast, scalable, and flexible data solutions.
SQL vs NoSQL: Features and Benefits
Feature | SQL | NoSQL | Hybrid / Multi-Model |
|---|---|---|---|
Definition | Relational, structured tables | Flexible, unstructured or semi-structured | Combines SQL and NoSQL capabilities |
Examples | PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle | MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis | CockroachDB, Cosmos DB |
Schema | Fixed | Flexible | Flexible + relational |
Transactions | Full ACID support | Limited / eventual consistency | ACID for transactions, flexible for analytics |
Scaling | Vertical | Horizontal | Horizontal for both workloads |
Performance | Excellent for structured queries | High for large/unstructured data | Balanced for transactional + analytics |
Use Cases | Finance, ERP, compliance-heavy apps | AI/ML, IoT, real-time analytics | SaaS, AI dashboards, multi-purpose cloud apps |
Cloud Readiness | Evolving | Cloud-native | Cloud-native with multi-region support |
Advantages | Reliability, data integrity | Flexibility, scalability | Combines strengths of SQL & NoSQL |
Disadvantages | Less flexible, harder to scale | Limited transactions | More complex, higher setup cost |
Databases for AI and Machine Learning
AI and ML rely on large and diverse datasets.

NoSQL is ideal for real-time, unstructured data such as social media feeds, IoT sensor data, or clickstream logs.
SQL is ideal for structured datasets used to train AI models.
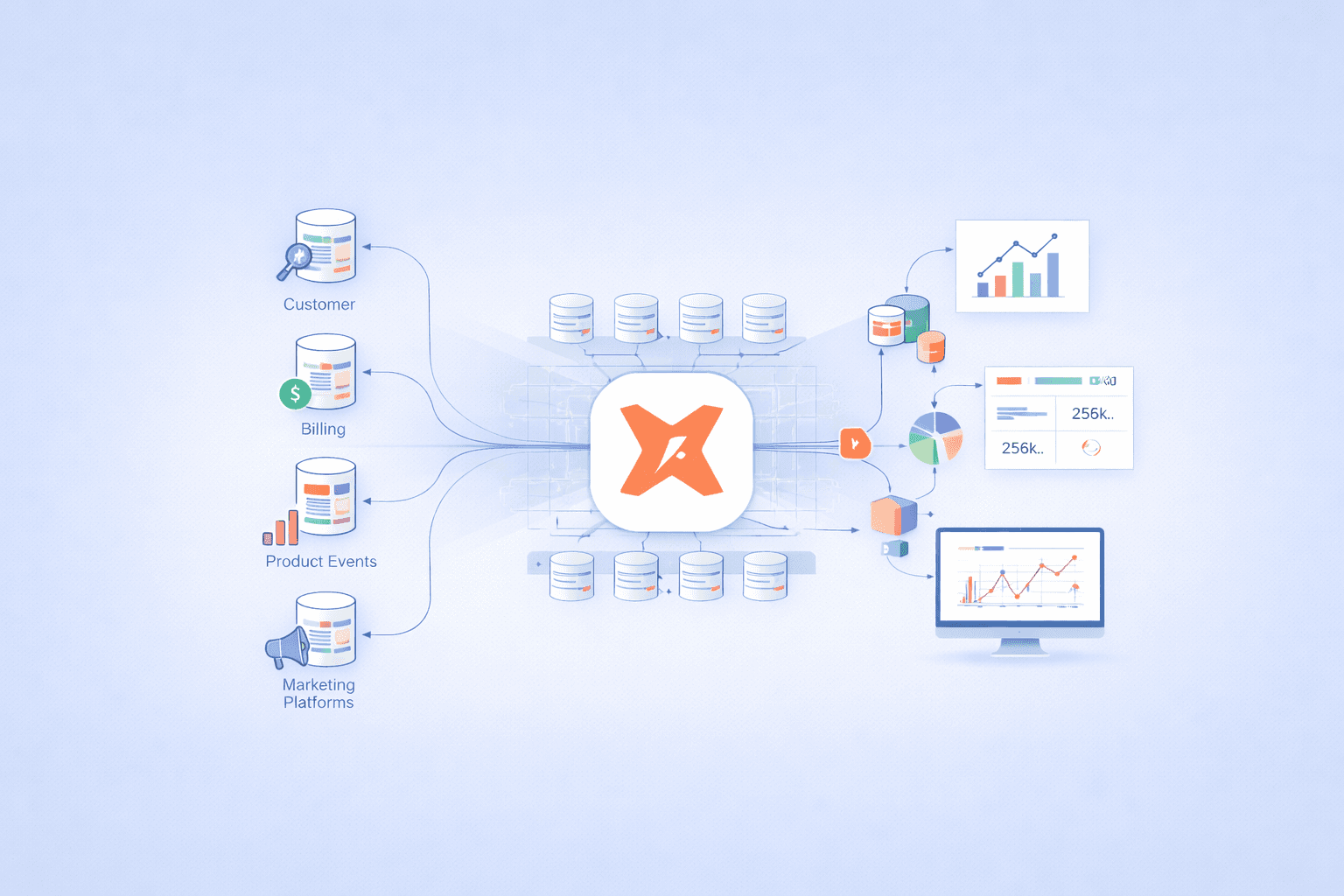
Platforms like Supaboard.ai leverage modern databases to power AI-driven business dashboards, combining speed with reliable structured data.
Takeaway
Use NoSQL for messy, real-time data. Use SQL for structured, high-quality training datasets.
Cloud-Native Applications and Database Choice
Modern SaaS, e-commerce, and streaming platforms need databases that can scale globally.
NoSQL handles unpredictable traffic spikes without downtime
Modern SQL solutions like Google Cloud Spanner or Azure Cosmos DB offer relational structure with horizontal scaling
Cloud-native solutions like Supaboard.ai dashboards integrate both SQL and NoSQL for seamless analytics at scale.
Takeaway
For global growth and unpredictable workloads, consider NoSQL or cloud-optimized SQL solutions.
Business Use Cases for SQL, NoSQL, and Hybrid Approaches
SQL Use Cases
Financial applications requiring precision and compliance
ERP systems with complex relational queries
Government systems managing citizen data
NoSQL Use Cases
IoT platforms managing millions of data points per second
Real-time analytics for e-commerce personalization
AI/ML data lakes feeding predictive models
Hybrid Use Cases
SaaS companies needing transactional integrity (SQL) and rapid analytics (NoSQL)
Takeaway
Align your database choice with business priorities, compliance requirements, and customer expectations.
Decision Flow: Choosing the Right Database
Do you need strict schema and compliance? SQL
Do you need flexibility and global scale? NoSQL
Do you need both transactional safety and scalability? Hybrid or multi-model solution
Takeaway
SQL and NoSQL are not rivals. They are choices on a spectrum depending on business needs.
Key Considerations Before Choosing a Database
Data Volume and Velocity: Steady transactions or massive real-time streams
Performance Needs: Latency-sensitive applications
Security and Compliance: HIPAA (link), GDPR (link)
Deployment Strategy: Cloud-native, hybrid cloud, or on-prem
Total Cost of Ownership: Licensing, infrastructure, maintenance
Future Database Trends Beyond 2025

Convergence of SQL and NoSQL for hybrid workloads
Multi-model adoption for flexibility
AI-driven autonomous databases
Edge and blockchain integration
Case Study: Mid-Sized SaaS Company
Challenge
Customers demanded real-time analytics
Platform required transactional reliability
Options Tested
PostgreSQL (reliable but harder to scale)
MongoDB (scalable but weak for transactions)
CockroachDB (hybrid)
Result
Chose CockroachDB hybrid solution
Reduced query latency by 50%
Cut infrastructure costs by 40%
Takeaway
Test databases with real workloads. Benchmarks alone do not capture real business needs.
FAQ
Is NoSQL better than SQL for all businesses?
No. SQL is essential where compliance, transactions, and structure matter.
Can SQL and NoSQL work together?
Yes, hybrid and multi-model databases are becoming standard.
Which industries prefer SQL?
Finance, healthcare, and government agencies.
Which database is best for cloud-native apps?
NoSQL or cloud-optimized SQL solutions.
Conclusion
Choosing a database is strategic, not a competition.
SQL: Structure, compliance, reliability
NoSQL: Speed, scale, flexibility
Hybrid: The future for most businesses
Future-proof your business by integrating structured and unstructured data, leveraging AI, and optimizing for the cloud. Platforms like Supaboard.ai demonstrate how smart database choices power business growth and actionable insights.